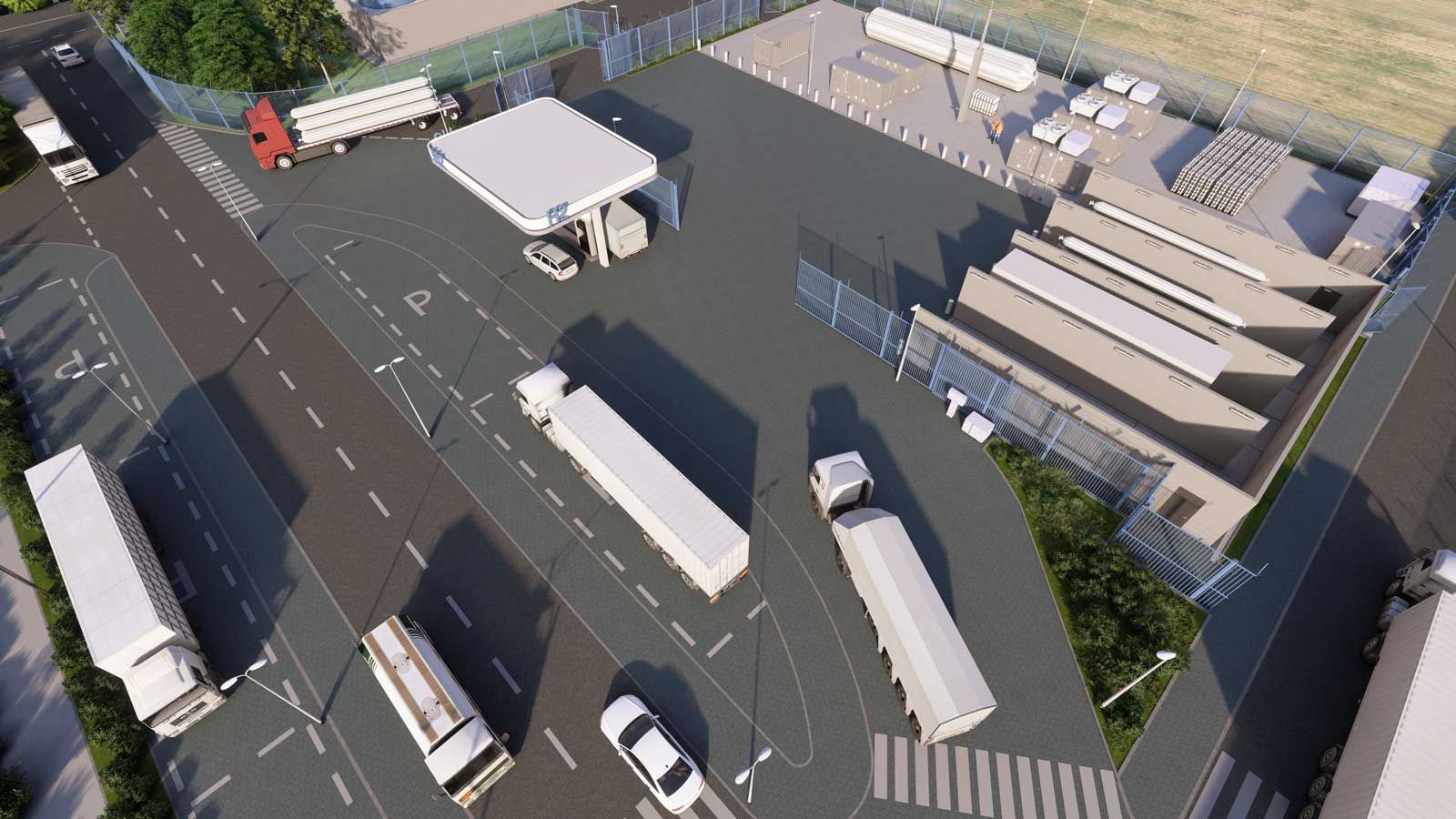
H₂ pilot plant in Lingen
Starting signal for green hydrogen production in Lingen.

What is hydrogen and why is it important?
Hydrogen is a naturally occurring chemical element that can be found in almost unlimited quantities on Earth. It is one of the building blocks of our universe. It is 14 times lighter than air, can be combusted without producing any CO₂ emissions and is not self-igniting, corrosive or radioactive. The importance of hydrogen lies primarily in its potential as a green energy source and feedstock. In addition to reducing CO₂ emissions in industrial plants, hydrogen and its derivatives can be used as a sustainable fuel for the transport sector.

Especially in the context of the energy transition, hydrogen is considered a storage and transport medium for renewable energies, with the prospect of replacing fossil fuels in many applications.
How is pure hydrogen obtained?
Pure hydrogen is produced by splitting hydrogen from various raw materials with the help of external energy input. Common methods include chemical conversion, such as steam reforming of natural gas, electrolysis of water, thermal processes, and newer approaches such as solar water splitting.
Particular focus is placed on the electrolysis of water, in which electrical energy is used to obtain hydrogen directly from water. If electricity from renewable sources is used in this process, the result is “green hydrogen.”
What do the different colours of hydrogen mean?
The colour classification of hydrogen defines both the production process and its carbon footprint: If the electricity produced by water electrolysis is sourced from renewables, such as wind or solar power, it is referred to as green hydrogen. Grey hydrogen, on the other hand, is produced conventionally using natural gas. If the carbon emissions produced in the process are not released but captured and stored, it is referred to as blue hydrogen. Less common is turquoise hydrogen, which entails thermal separation of methane, creating solid carbon rather than climate-damaging carbon dioxide.
Hydrogen plays a key role in the decarbonisation of energy-intensive sectors. In addition to reducing CO2 emissions in industrial processes, hydrogen could be used as a sustainable fuel in the transport.
The ever-increasing interlinking of potential applications – electricity and heat, transport and industry – is referred to as sector coupling.
Green hydrogen produced by regenerative energy in particular is considered a key technology in the drive for climate neutrality.
Thanks to the increasing linkage of sectors, green hydrogen can make a significant contribution to achieving a holistic and sustainable energy supply.


Together with partners from other sectors, companies and associations, RWE is currently pressing ahead with numerous green hydrogen projects in Europe. Find out where and how RWE is shaping progress in this area and setting the course for a climate-neutral hydrogen economy. A key example of this is the energy location Lingen, where several hydrogen projects are currently being realised.
RWE wants to support industrial and mobility businesses switch to green hydrogen. Therefore, RWE is going to be making the fuel available via hydrogen filling stations as well as hydrogen tank trucks and via pipelines.
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us directly.





We are happy to answer questions on hydrogen and our projects.