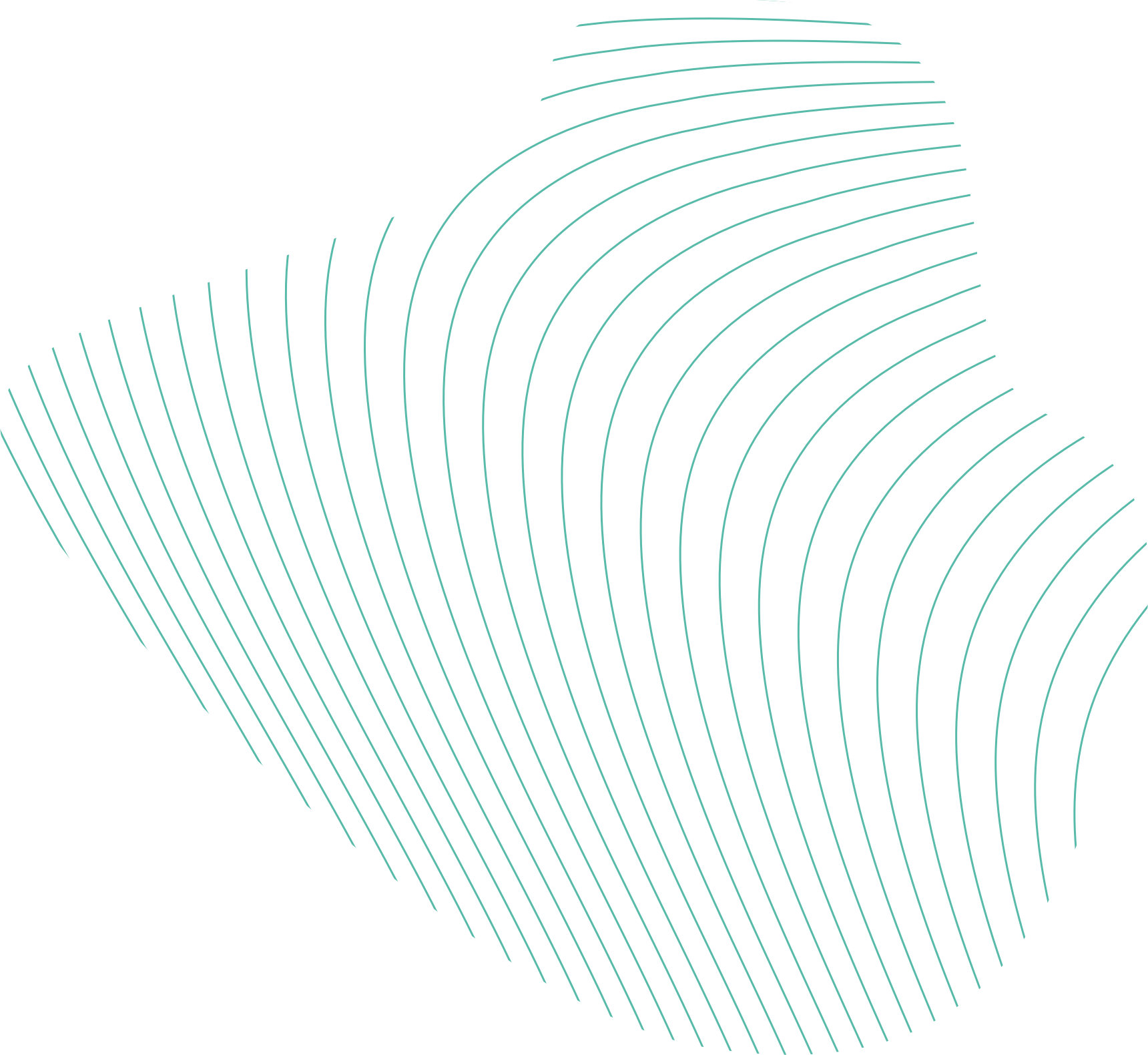

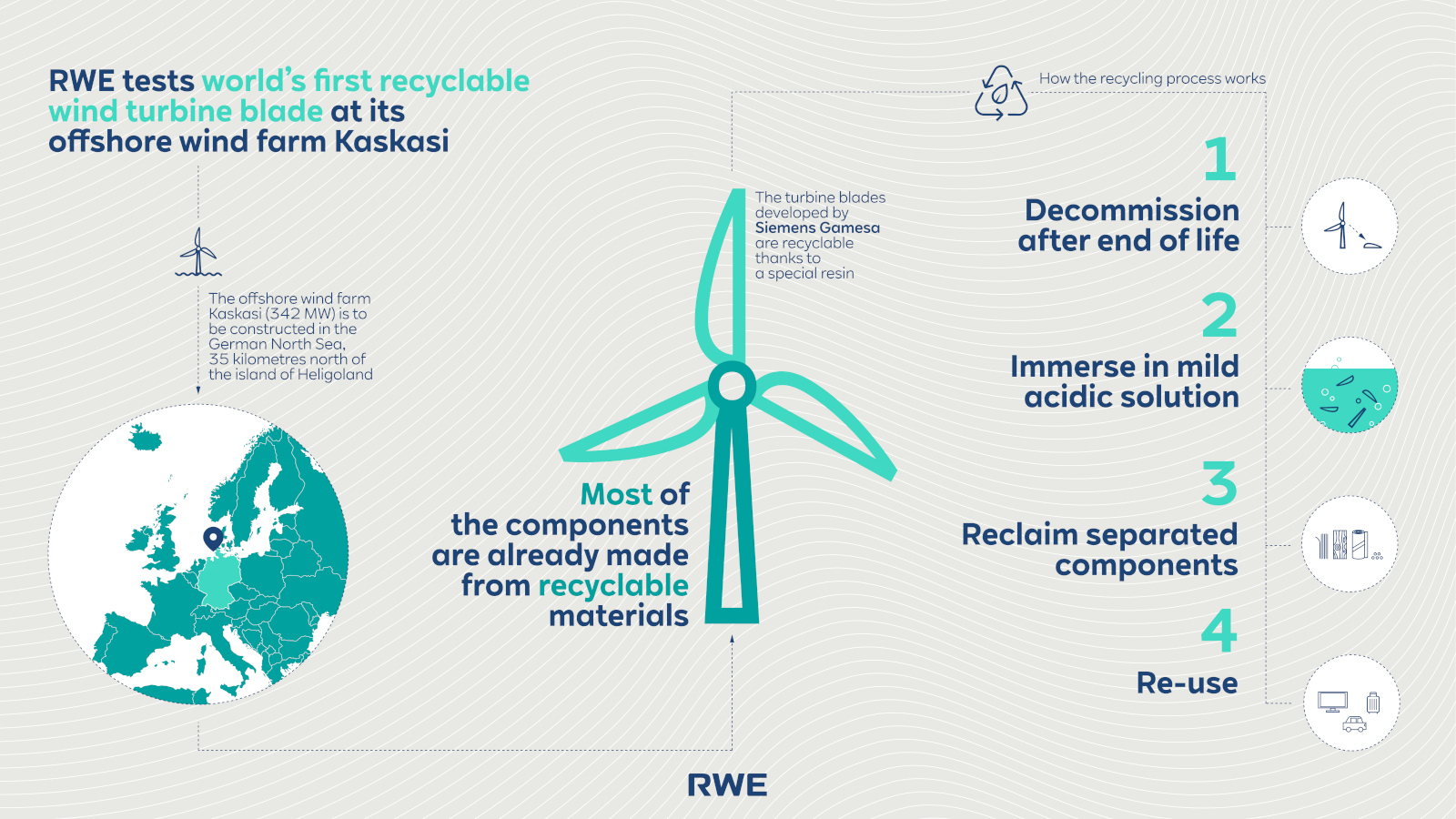
Wind energy is considered one of the most important pillars in the transition to a sustainable energy supply. While the majority of a wind turbine is already easily recyclable today the rotor blades pose a particular challenge. They are made of complex composite materials that have been difficult to separate from each other. Currently, only a few recycling solutions are being developed to prevent decommissioned blades from ending up as waste in landfills. However, RWE is investing in a particular approach which focusses on "design for recycling". This approach takes sustainability into account right from the start of a wind turbine's life cycle. It also underlines RWE's ambition to improving circular economy by refurbishing turbine components whenever possible or by returning them to the raw material cycle, thereby conserving resources and protecting the environment.
The key to the enhanced recyclability of Siemens Gamesa’s new rotor blades lies in an innovative resin. While conventional resins create a permanent bond, the new resin can be dissolved at the end of its service life – in a particularly gentle and efficient manner.
The process consists of four steps:
Through these projects, RWE showcases how technological innovation and environmental responsibility go hand in hand. By setting industry-leading practices, RWE is driving progress that extends beyond individual wind farms, laying the foundation for a more sustainable energy future.
RWE is using the recyclable rotor blades in various large-scale projects, thereby actively contributing to the further development of sustainable wind energy:
At our offshore wind farm Sofia, more than half of the total 100 turbines are being equipped with recyclable rotor blades – an internationally acclaimed showcase project. Thanks to close cooperation with Siemens Gamesa, recyclable rotor blades have been installed on a large scale in the UK for the first time, bringing the circular economy in wind energy within reach.
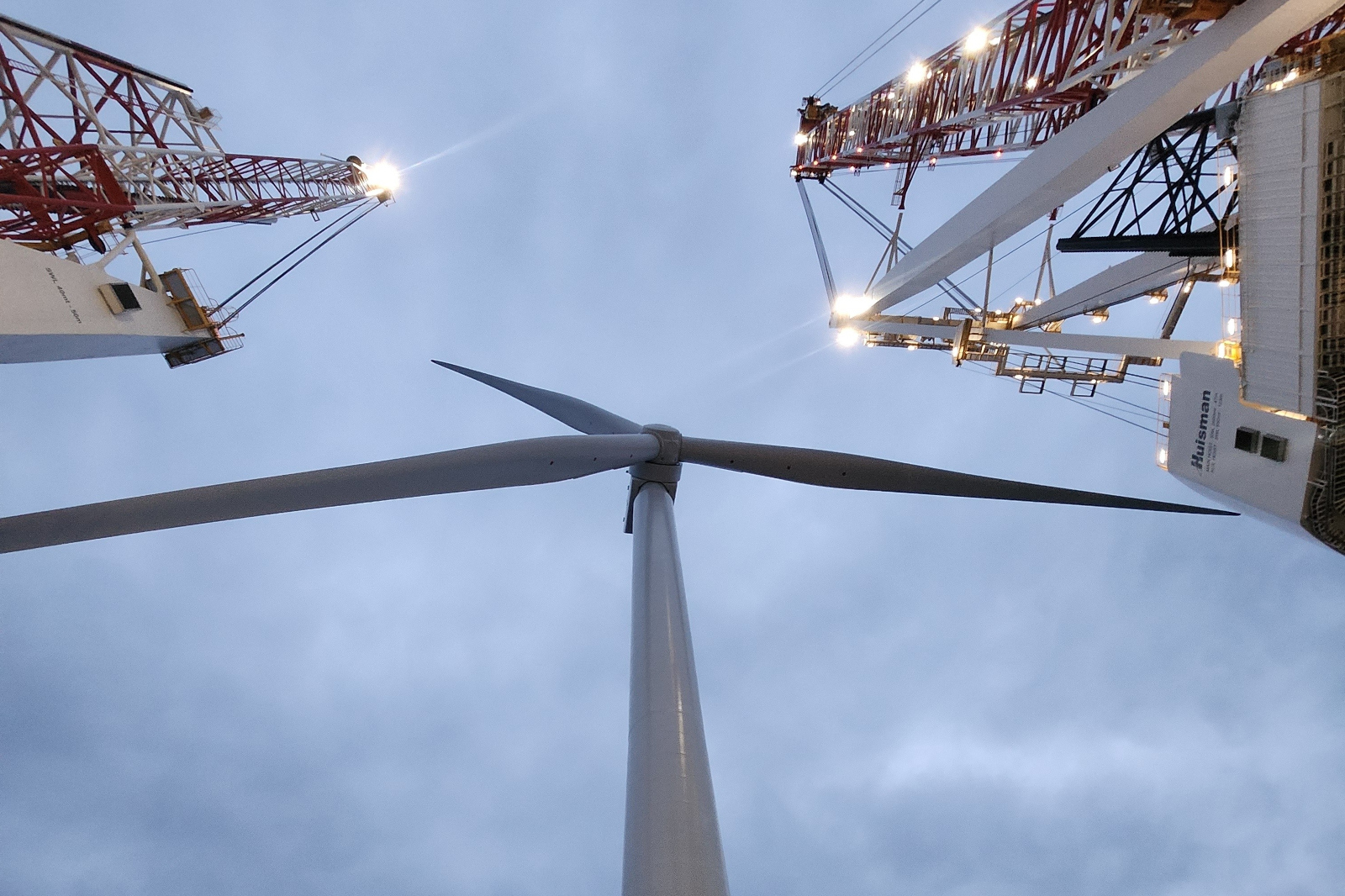

Kaskasi serves as a ‘research laboratory’ for sustainable wind power solutions. Among other innovations, the recyclable rotor bladeswere used here for the very first time, forming the basis for large-scale applications.
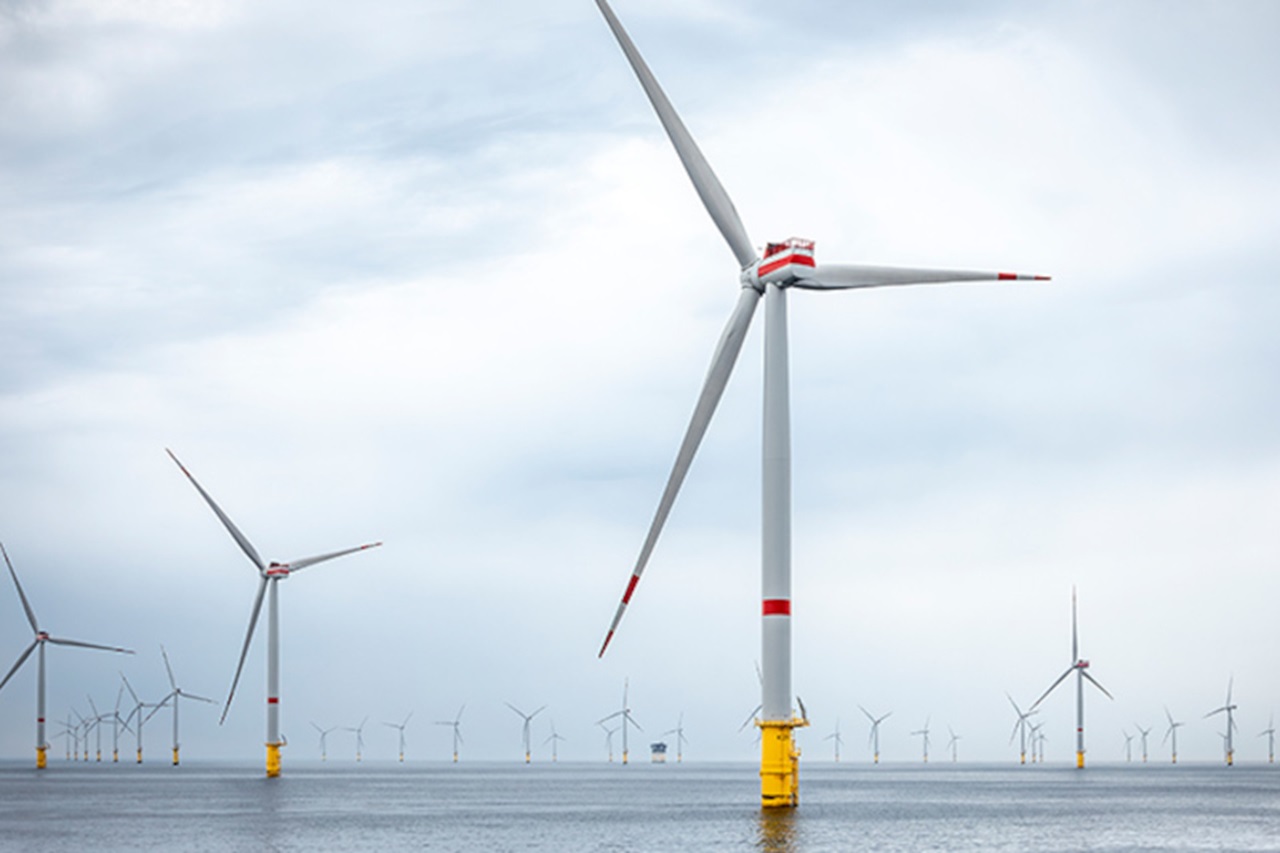

In the Danish Thor project, RWE is using recyclable rotor blades and steel towers made of CO2-reduced materials. The plan is to install a total of 40 turbines with 120 recyclable rotor blades, combining innovation and climate protection.
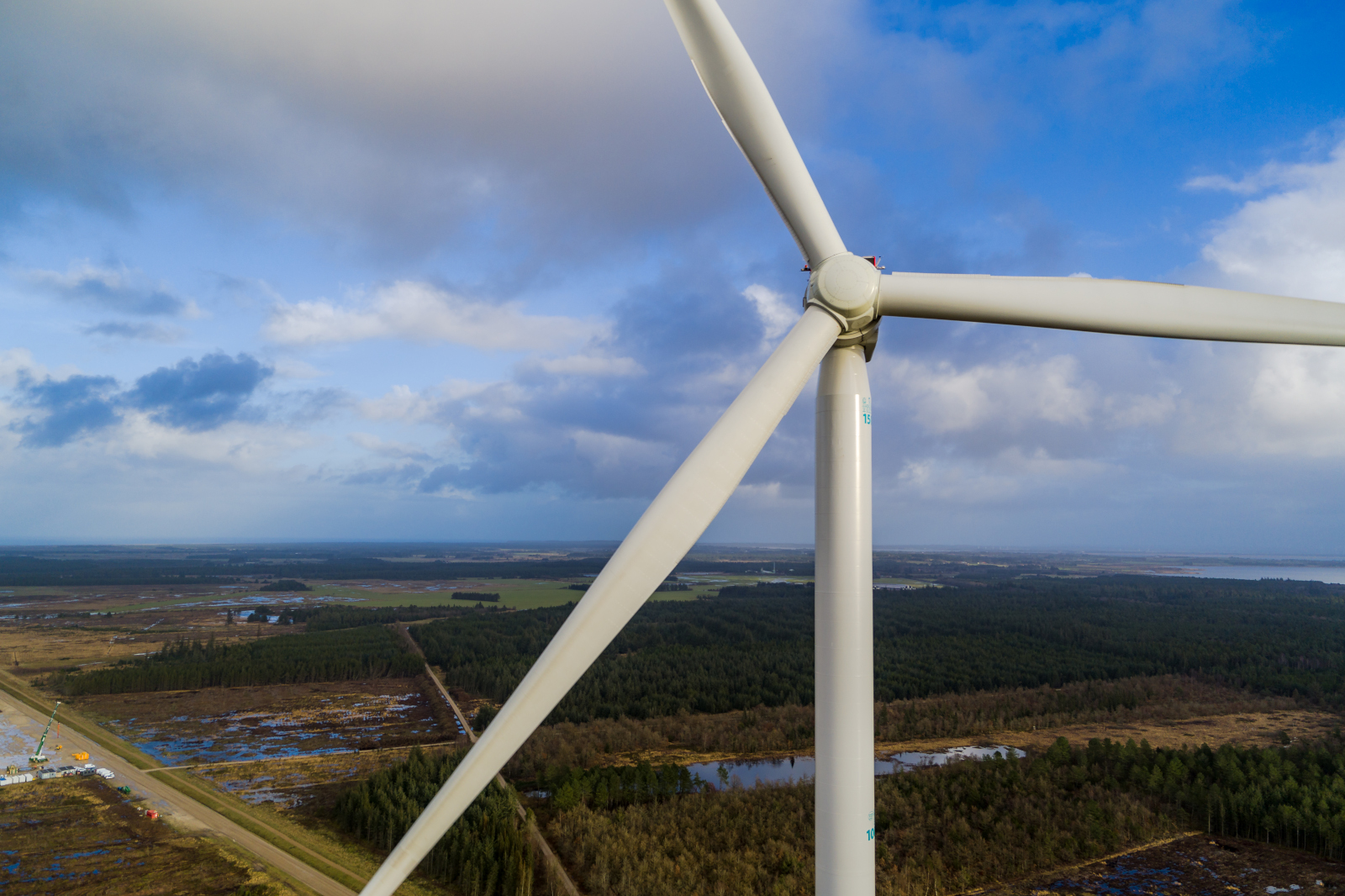

Through these projects, RWE showcases how technological innovation and environmental responsibility go hand in hand. By setting industry-leading practices, RWE is driving progress that extends beyond individual wind farms, laying the foundation for a more sustainable energy future.

